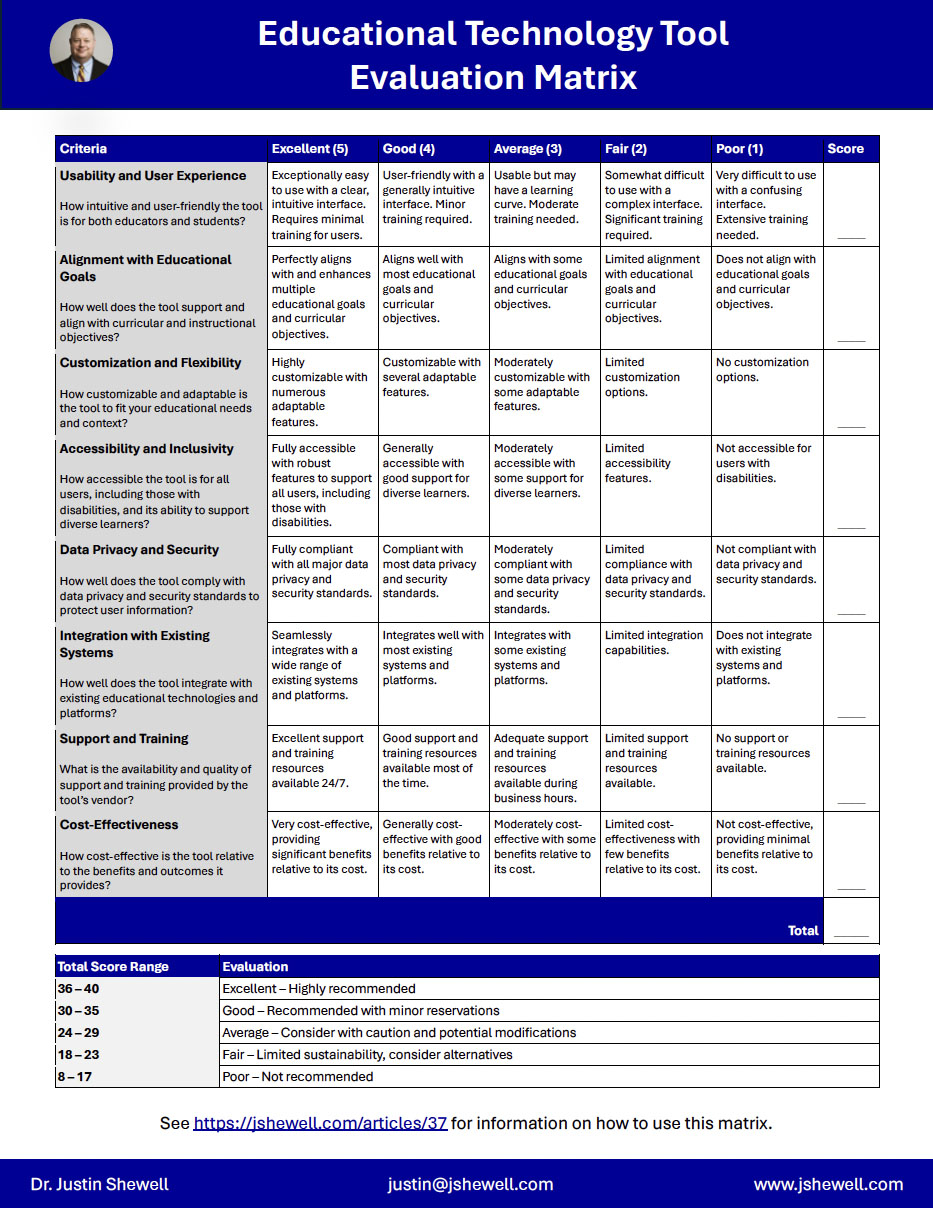
In the ever-evolving landscape of educational technology, selecting the right tools to enhance teaching and learning can be daunting. The following matrix provides a structured and comprehensive approach to assess various technology tools, ensuring they align with your educational and administrative goals. This guide will walk you through the criteria in the evaluation matrix, offering descriptions and practical examples to help you make informed decisions.
Usability and User Experience
This criterion helps assess how intuitive and user-friendly the technology tool is for all users, including administrators, teachers and students. When you are looking at the usability of the tool, keep in mind the following:
Navigation
- Clear Menus and Links: Ensure the navigation menus and links are clearly labeled and easy to find. Users should be able to understand where each link will take them without confusion.
- Consistent Navigation Structure: The tool should maintain a consistent navigation structure throughout the tool to help users learn and predict where to find information.
- Ease of Navigation: The tool uses breadcrumb trails or another mechanism to show users their current location within the tool and allow easy navigation back to previous sections.
- Search Functionality: The tool should include a robust search function that allows users to quickly find specific content or features within the tool.
Layout
- Simple and Clean Design: The tool should use a clean and uncluttered layout that avoids overwhelming users with too much information at once.
- Logical Grouping: The tool should group related content and features logically to make it easier for users to find what they need.
- Responsive Design: Ensure the tool is responsive and works well on various devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Appropriate Use of Colors and Text
- Readable Fonts: The tool should use clear, readable fonts and appropriate font sizes to ensure text is easy to read. Avoid overly decorative fonts that can hinder readability.
- Color Contrast: The tool should use high contrast between text and background colors to enhance readability. Ensure color choices are accessible to users with color blindness.
- Consistent Color Scheme: The tool should maintain a consistent color scheme throughout the tool to create a cohesive look and feel.
User Instructions
- Clear Instructions: The tool sholud provide clear, concise instructions for using the tool’s features. Use step-by-step guides where necessary.
- Onboarding Process: The tool should implement an onboarding process for new users that guides them through the main features and functionalities of the tool.
- Tooltips and Pop-up Help: Use tooltips and pop-up help messages to provide additional information and guidance without overwhelming the user.
Help Option
- Help Center: The tool should include a comprehensive help center or support section that users can access at any time. This should contain FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and user manuals.
- Interactive Tutorials: The tool should offer interactive tutorials or guided walkthroughs to help users learn how to use the tool effectively.
- Contact Support: The tool should provide an easy way for users to contact support, such as a live chat option, email support, or a dedicated support phone line.
- Feedback Mechanism: The tool should include a feedback mechanism that allows users to report issues, suggest improvements, or ask for additional help.
Alignment with Educational Goals
This criterion helps determine how well the tool supports and aligns with curricular and instructional objectives. When considering alignment, it is important to consider both positive and negative alignment. Positive alignment refers to how well the tool supports the curruicular and instructional objectives. For example, if you are a evaluating a tool to support the writing efforts of your students, the tool should, of course, enhance students writing skills and provide robust support for learning of grammar, style, coherence, diction, and other elements of writing. Negative alignment refers to any aspects of the tool that might detract from accomplishing your curricular and instructional objectives. Going back to the writing tool example, if the tool requires a steep learning curve, or provides incorrect instruction on grammar, it will detract from your objectives. There might also be aspects of the tool that impact objectives other than writing. For example, students might become over-reliant on the tool and resist developing their own grammar and writing skills. The tool might also only provide surface-level corrections and not help students make deeper connections in their writing.
Customization and Flexibility
This criteria is designed to measure the ability of the tool to be customized and adapted to fit specific educational needs and contexts. When evaluating customization and flexibility, keep in mind the following:
Content Adaptability
- Custom Lessons and Activities: Can educators create, modify, and personalize lessons and activities to suit different learning levels and styles?
- Editable Content: Does the tool allow for the customization of existing content to align with specific curricular goals and classroom needs?
User Roles and Permissions
- Role-Based Access: Can the tool be configured to provide different levels of access and functionality for teachers, students, and administrators?
- Permission Settings: Are there customizable permission settings to control who can view, edit, and manage content and data?
Interface Customization
- Personalized Dashboards: Can users customize their dashboards or interfaces to highlight the most relevant information and tools for their roles?
- Theme and Layout Options: Are there options to customize the appearance, such as themes, colors, and layouts, to better match school branding or personal preferences?
Integration with Other Tools
- Third-Party Integrations: Does the tool integrate seamlessly with other educational technologies and platforms, such as Learning Management Systems (LMS), grading systems, and communication tools?
- APIs and Plugins: Are there available APIs or plugins that allow for further customization and integration with other software?
Adaptability to Different Teaching Models
- Support for Various Instructional Strategies: Can the tool support a range of instructional strategies, such as flipped classrooms, blended learning, project-based learning, and individualized instruction?
- Scalability: Is the tool scalable to accommodate different class sizes and diverse educational settings, from small groups to large classes?
Multilingual Support
- Language Options: Does the tool offer support for multiple languages, enabling use in diverse linguistic contexts?
- Localization Features: Are there localization features that adapt content and interfaces to different cultural and educational contexts?
Accessibility and Inclusivity
This criteria measures the tool’s accessibility for all users, including those with disabilities, and its support for diverse learners. When evaluating accesibility and inclusivity, keep in mind the following:
Compliance with Accessibility Standards
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): Ensure the tool adheres to WCAG standards, which provide guidelines for making web content more accessible to people with disabilities.
- Section 508 Compliance: If you are in the United States, verify that the tool complies with Section 508 standards, ensuring it is accessible to individuals with disabilities in federal programs. If you are outside the United States, verify the tool complies with any accessibility laws that exist in your country. You may wish to the use the Section 508 guidelines as a model if your country doesn't have any laws or guideline regarding serving those with disabilities.
Assistive Technology Compatibility
- Screen Readers: Check if the tool is compatible with screen readers such as JAWS, NVDA, or VoiceOver, which assist visually impaired users.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure the tool can be fully navigated using a keyboard, without requiring a mouse, to support users with motor disabilities.
- Speech Recognition: Assess compatibility with speech recognition software for users who rely on voice commands to interact with the tool.
Text and Visual Accessibility
- Alt Text for Images: Ensure all images and graphics include descriptive alt text to support users with visual impairments.
- High Contrast Modes: Provide high contrast modes to make text and visual elements easier to see for users with low vision.
- Resizable Text: Allow users to adjust text size without loss of content or functionality to accommodate varying levels of visual ability.
Multilingual Support
- Language Options: Offer multiple language options to accommodate users from diverse linguistic backgrounds.
- Cultural Relevance: Include culturally relevant examples and content to make the tool more inclusive for users from different cultural contexts. Also ensure any cultural examples used are applicable across cultures and do not confuse those from cultures outside that of those given in the tool.
Data Privacy and Security
This criteria assesses how well the tool complies with data privacy and security standards to protect user information. When evaluating this criteria, keep in mind the following:
Compliance with Legal Standards
- FERPA Compliance: Ensure the tool complies with the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), protecting the privacy of student education records.
- GDPR Compliance: For tools used in the European Union, verify compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which governs data protection and privacy.
Data Collection Practices
- Minimal Data Collection: Assess whether the tool collects only the necessary data required for its functionality and avoids excessive data collection.
- Data Usage Transparency: Ensure the tool provides clear information about what data is collected, how it is used, and who it is shared with.
User Consent and Control
- Informed Consent: Verify that the tool obtains explicit, informed consent from users (or their guardians) before collecting or using their data.
- Data Control: Check if users have the ability to access, correct, or delete their personal data from the system.
Privacy Policy
- Clear Privacy Policy: Evaluate the tool’s privacy policy for clarity and completeness. It should be easily accessible and understandable for users.
- Third-Party Sharing: Determine if and how the tool shares data with third parties and ensure it complies with privacy standards.
Data Encryption
- In-Transit Encryption: Ensure that data transmitted between the user and the tool’s servers is encrypted using protocols like SSL/TLS. The URL, or web address for the tool, if it is browser-based, should begin with HTTPS. If the tool is NOT browser-based, ask the vendor how the data is encrypted during transit.
- At-Rest Encryption: Verify that data stored on the tool’s servers is encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. The vendor can provide that information.
Access Controls
- User Authentication: Assess the strength of user authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to prevent unauthorized access. Does the tool require students to use a secure password that they change at least once every three months?
- Role-Based Access: Check if the tool implements role-based access controls, ensuring that users only have access to data relevant to their roles.
Data Breach Response
- Incident Response Plan: Determine if the tool has a clear and effective data breach response plan in place to quickly address and mitigate the effects of any data breaches. The vendor can provide that information.
- User Notification: Verify that the tool has procedures to promptly notify users in the event of a data breach. The vendor can provide that information.
Security Audits and Certifications
- Regular Audits: Check if the tool undergoes regular security audits by third-party organizations to identify and address vulnerabilities. That information should be available from the vendor.
- Security Certifications: Look for security certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, which indicate a high standard of data security practices. That information should be available from the vendor.
Integration with Existing Systems
This criteria evaluates how well the tool integrates with existing educational technologies and platforms. When evaluating this criteria, keep in mind the following:
Learning Management System (LMS) Integration
Ensure the tool integrates smoothly with the LMS platform used in your setting. Common LMS platforms like Canvas, Moodle, Blackboard, and Google Classroom, allow many integrations. Check if the tool can synchronize grades, assignments, and student data automatically.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Verify if the tool supports SSO to allow users to access the tool using their existing credentials. This prevents the need to create an additional username and password combination that may lead to unauthorized access if the tool is hacked or there is a security breach. Students also do not need to remember an additional password, making the tool easier to use.
Student Information System (SIS) Integration
Check if the tool can integrate with your existing SIS. Common SIS platforms include PowerSchool, InfiniteCampus, and Skyward. The tool may need to push and pull student information, schedules, and other relevant data to work effectively. This process should be automated.
Communication Tools
Ensure the tool can integrate with existing communication tools like email and messaging platforms such as Slack and Microsoft Teams. This facilitates easy communciation and notifications. The tool should be able to send out automatic notifications and updates to users, including students, parents, faculty, and administrators through existing communication channels.
Common Data Formats
Ensure the tool supports common data formats such as CSV, XML, or JSON formatted data for easy import and export of data to other tools. Ideally, the tool should adhere to interoperability standards such as the IMS Global Learning Tools Interoperability (LTI), which facilitate seamless integration with other technologies.
Analytics and Reporting Integration
Ensure the tool can integrate with existing reporting and analytics systems and allows for easy data export to other analytics tools.
Support and Training
This criteria measures the availability and quality of support and training provided by the tool’s vendor. When evaluating this criteria, keep the following in mind:
Availability of Support
- Multiple Channels: Ensure the tool offers multiple support channels, such as email, phone, live chat, and a support ticket system.
- 24/7 Availability: Check if customer support is available 24/7, especially if the tool is used across different time zones or in a critical educational setting.
Response Time and Quality
- Quick Response Time: Evaluate the average response time for support requests to ensure timely assistance.
- Quality of Support: Assess the quality of responses, including the accuracy, clarity, and helpfulness of the support provided.
Training Resources
- Documentation: Look for detailed user manuals, FAQs, and step-by-step guides that cover all aspects of the tool.
- Video Tutorials: Check for video tutorials that provide visual instructions on how to use the tool’s features.
- Onboarding Programs: Evaluate if the tool offers structured onboarding programs to help new users get started quickly.
- Implementation Assistance: Assess the level of support provided during the implementation phase, including setup and configuration help.
Professional Development Opportunities
- Regular Webinars: Look for regular webinars that provide in-depth training on specific features and best practices.
- Workshops: Check if the vendor offers hands-on workshops, either in-person or virtual, to provide more interactive training.
- User Certification: See if the tool offers certification programs for educators, helping them become proficient users and recognized experts.
- Continuing Education: Evaluate opportunities for continuing education to keep up with updates and new features.
Community and Peer Support
- Active Forums: Check for active user forums where educators can share tips, ask questions, and learn from each other’s experiences.
- Social Media Groups: Look for social media groups or communities that provide additional support and networking opportunities.
- User Groups: Assess the availability of user groups or networks that facilitate peer collaboration and support.
- Mentorship Programs: Check if the vendor offers mentorship programs that connect new users with experienced ones.
Cost-Effectiveness
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of an educational technology tool involves assessing the value it provides relative to its cost. Consider the following suggestions to ensure that the investment in the tool is justified and beneficial in your context:
Initial Purchase Price
- Licensing Fees: Evaluate the initial cost of purchasing or licensing the tool, including any one-time fees.
- Hardware Requirements: Consider any additional hardware costs required to use the tool effectively, such as computers, tablets, or VR headsets.
Ongoing Costs
- Subscription Fees: Check for recurring subscription fees, such as annual or monthly charges.
- Maintenance and Support Costs: Account for costs related to maintenance, updates, and customer support.
Implementation Costs
- Setup and Configuration: Assess the costs associated with setting up and configuring the tool for your institution.
- Training and Professional Development: Consider the costs of training staff and providing ongoing professional development to ensure effective use of the tool.
Educational Impact
- Learning Outcomes: Evaluate the tool’s effectiveness in improving student learning outcomes and achieving educational goals.
- Teacher Efficiency: Assess how the tool enhances teacher efficiency, such as reducing grading time or streamlining administrative tasks.
Student Engagement
- Engagement Levels: Determine how well the tool engages students and motivates them to participate actively in learning activities.
- User Satisfaction: Collect feedback from students and teachers to gauge their satisfaction with the tool and its impact on their educational experience.
Scalability
Assess the tool’s ability to scale and accommodate growing student populations and additional features without significant additional costs. Consider how adaptable the tool is to changing educational needs and technologies, ensuring it remains relevant and valuable over time.
Comparative Analysis
- Alternative Solutions: Compare the cost and benefits of the tool with alternative solutions, including other similar tools or traditional methods.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the ROI by comparing the total costs to the measurable benefits, such as improved test scores, increased student engagement, or time saved.
- Longevity: Assess the tool’s potential longevity and whether it will remain useful and relevant for several years.
- Upgrade and Expansion: Evaluate the cost and ease of upgrading the tool or expanding its functionality as needs evolve.